SSDs have completely revolutionized the way we store files on devices. The portable size with relatively more capacity, speed, and agility of SSDs have almost replaced the traditional magnetic disk hard drives.
SSDs store data in NAND flash devices that store a small quantity of charge on a floating gate when the cell is programmed. This charge is expected to last long without any power backup. This is the main reason behind ssd storing data without any power.
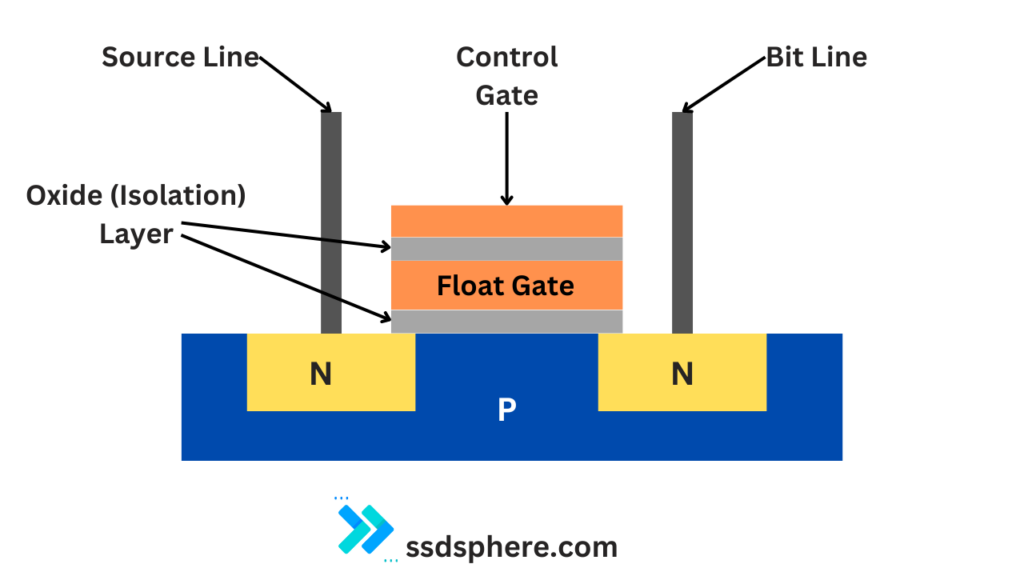
The key to NAND flash memory‘s ability to retain data without power lies in the floating-gate transistor. Each transistor has two gates: the control gate and the floating gate.
The floating gate, sandwiched between the control gate and the transistor channel, is insulated by a layer of oxide. This insulation is crucial as it traps electrons in the floating gate.

How do SSD store data without any Power?
Basics of Data Storage
First, let’s start with the basics of how data is stored. Computers store data in binary format, which means everything is represented as a series of 0s and 1s. Each 0 or 1 is a bit, and a group of 8 bits forms a byte.
Traditional Hard Drives vs. SSDs
Traditional hard drives (HDDs) store data on spinning disks. They use magnetism to store these bits. When power is lost, the magnetism remains, and so does the data.
SSDs, on the other hand, do not have moving parts. They use a technology called NAND flash memory.
NAND Flash Memory
- NAND Flash Memory Structure: NAND flash memory, which is the heart of an SSD, is made up of cells. Each cell stores bits.
- Types of Cells:
- SLC (Single-Level Cell): Stores 1 bit per cell.
- MLC (Multi-Level Cell): Stores 2 bits per cell.
- TLC (Triple-Level Cell): Stores 3 bits per cell.
- QLC (Quad-Level Cell): Stores 4 bits per cell.
- How Cells Store Data: Each cell in NAND flash memory contains a floating gate transistor. This transistor can hold an electrical charge.
- Storing Bits:
- Writing Data: When data is written to an SSD, electrons are pushed into the floating gate. The presence or absence of these electrons represents a 1 or a 0.
- Charge Trapping: The key aspect here is that these cells can trap these electrons even when power is not supplied. This is how the SSD maintains your data even when it’s turned off.
- Reading Data: When the SSD needs to read the data, it checks whether there’s a charge in the floating gate. If there’s a charge, it might read it as a 1; no charge would be a 0 (this can vary depending on the design).
- Durability and Wear: Over time, pushing electrons in and out of the floating gate wears down the cell. This is why SSDs have a limited number of write cycles, but for most users, this is not an immediate concern.
So how does SSD work in actuality?
Basic Physics Concepts
- Electrons and Charge: At a fundamental level, data storage in NAND flash memory involves manipulating electrons, which are negatively charged particles.
- Semiconductors and Transistors: NAND flash memory is made from semiconductor materials, typically silicon. Transistors, which are the basic building blocks of NAND flash memory cells, can switch current on and off or amplify current, and they form the basis of digital electronics.
Structure of NAND Flash Memory Cells
- Floating Gate Transistor: Each cell in NAND flash memory contains a floating gate transistor. The key parts of this transistor are:
- Control Gate: The external part of the transistor that controls the flow of electrons.
- Floating Gate: A conductive gate that is electrically isolated (i.e., not connected to any circuit). It’s between the control gate and the channel of the transistor.
- Source and Drain: Regions in the silicon where electrons enter and exit.
- Insulating Layers: The floating gate is surrounded by insulating layers (usually silicon dioxide) that prevent electrons that have entered the floating gate from escaping easily.
Storing Data (Writing)
- Electron Tunneling: To store data (write), electrons are forced from the semiconductor channel into the floating gate. This is done using a process called “Fowler-Nordheim tunneling”.
- High Voltage: A high voltage is applied to the control gate, which creates a strong electric field.
- Quantum Tunneling: This field causes electrons to quantum tunnel through the insulating layer to the floating gate.
- Charge Trapping: Once in the floating gate, electrons are trapped due to the insulating properties of the surrounding material. This changes the threshold voltage of the transistor.
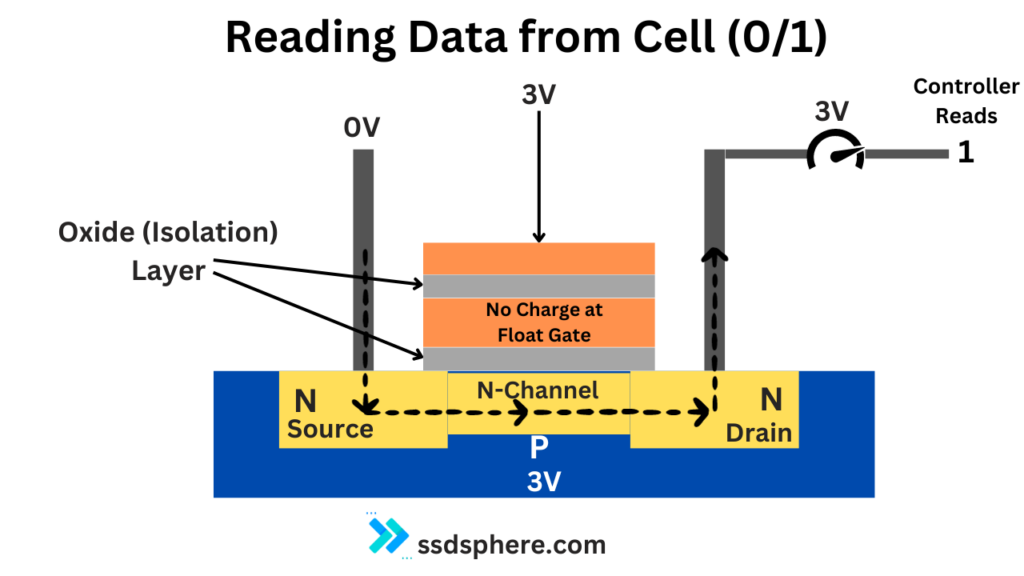
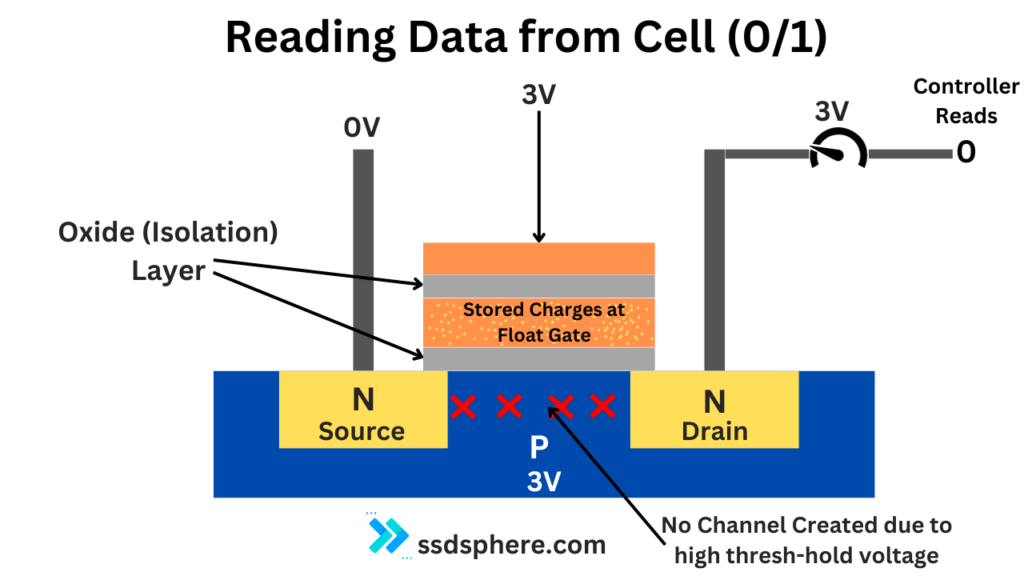
Reading Data
- Threshold Voltage: The presence or absence of electrons in the floating gate alters the transistor’s threshold voltage (the voltage at which the transistor turns on).
- Determining 0s and 1s:
- With Electrons (Charged): If the floating gate has trapped electrons, it requires a higher voltage to activate the transistor. This state can be read as a ‘1’.
- Without Electrons (Not Charged): If the floating gate has no electrons, a lower voltage can activate the transistor. This state is read as a ‘0’.
- Reading Process: During a read operation, a specific voltage is applied to the control gate. The transistor’s ability to conduct current at this voltage is then measured. Based on whether the current flows or not, the SSD controller can determine whether the cell is in a ‘0’ or ‘1’ state.
How Long Can A SSD Store My Data Without Power?
According to JEDEC standards, data on ssd should be available after 1 year a at temperature of 30 degrees Celsius. The Enterprise SSDs are expected to store data for a longer period.
As discussed above, SSDs store data by inserting electrons into the NAND gate. The main reason behind the disappearance of data is the leakage of electrons due to the phenomenon of quantum tunneling. Most of the time it becomes impossible to recover data from an SSD if it had no power for several years.
Precisely, this time is indefinite and cannot be predicted. You can expect your SSD to retain your data for 2-5 years minimum. Manufacturers claim this period is around 15-20 years but this comes with multiple strings attached.
A certain statement is that you can’t expect an SSD to store your data for a lifetime without any power.
So, what is the reason behind the data retention?
The programmable charge trap cells are responsible for the data storage. Although these cells can hold either 0s or 1s when we combine them in a big number, massive data can be stored inside a single NAND Flash Chip.
These stored charges stay inside the cells for years but if for any reason the cell’s power is not restored, you can hardly do anything to restore that data. Normally, your SSD will not lose that data for around 5 years and that is a huge amount of time.
These NAND Flash Cells or chips are known as non-volatile memory. The main purpose of this non-volatile memory is to retain the data even without the power. So, there is nothing to be very serious about that.
Also, there is nothing you can do to find the exact time of data retention any SSD can offer without the power supply.
Factors Affecting SSD Data Retention
| Factor | Impact on Data Retention | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Type of NAND Flash | High | Different NAND types offer varying retention capabilities |
| Age and Usage | High | Older and more frequently used SSDs may have shorter retention times |
| Storage Conditions | High | Temperature and humidity can significantly affect retention |
| Manufacturing Quality | Medium | Higher quality SSDs tend to retain data longer |
| Data Density | Medium | Higher density (TLC, QLC) may result in shorter retention times |
| Drive’s Firmware and Error Correction | Low to Medium | Can impact how well the drive maintains and recovers data |
SSD Data Retention Comparison by NAND Type
| NAND Flash Type | Description | Estimated Data Retention Period |
|---|---|---|
| SLC (Single-Level Cell) | Stores 1 bit per cell; Higher durability and performance | 2+ years |
| MLC (Multi-Level Cell) | Stores 2 bits per cell; Balanced performance and cost | 1-2 years |
| TLC (Triple-Level Cell) | Stores 3 bits per cell; Lower cost, higher density | 1 year |
| QLC (Quad-Level Cell) | Stores 4 bits per cell; Highest density, lower endurance | 6 months – 1 year |
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, frequent writing to an SSD can wear out the NAND flash memory cells, reducing the drive’s overall lifespan.
To extend an SSD’s lifespan, avoid unnecessary writing operations, ensure good cooling, keep your firmware updated, and don’t fill the drive.
For long-term storage, keep the SSD in a cool, dry place and ideally store it with a full charge. It’s also a good idea to power it up occasionally to maintain data integrity.
Great article. Nicely explained.
Thanx Vishnu